Sodium saccharin, scientific name is o-benzoyl sulfonyl imide sodium, also known as soluble saccharin, is the sodium salt of saccharin, showing a white powder, odorless or slightly scented, sweet and bitter taste. As the earliest discovered artificial sweetener, saccharin is a very interesting “cornerâ€. Its sweetness is about 500 times that of sucrose, and it was buoyed by the market once it came out, but it was subsequently regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the 1970s. This product may be harmful to health. This product contains saccharin that can cause cancer in experimental animals."
What exactly is this matter about
The story begins with the "discovery" of saccharine. According to legend, one day in 1879, in the laboratory of the Hopkins University in the United States, the Russian chemist Faridad Berger was working on the synthesis of aromatic sulfonic acid compounds. At dinner, he may have forgotten to wash his hands. He unexpectedly discovered that the steak was sweet and the cutlery was sweet, but the dinner did not add sugar. The sweetness was actually related to the pencil he had written in the lab. Subsequently, Faridad Berger found that the sweetness came from a chemical called sodium sulfonimide. After many setbacks, Faridad Berger eventually extracted a particularly sweet white crystal from coal tar, which he called "saccharin."
There are probably more than one story versions of saccharine "discovered." The above is just one of them. However, no matter how it is said, saccharin cannot change the “origin†of an organic chemical synthesis product, because the main raw materials of saccharin are toluene, chlorosulphonic acid, o-toluidine, etc., all of which are petrochemical products. Whether it would be harmful to human health or not, more animal experiments have indicated that saccharin sodium may cause bladder cancer, and then led to the United States Food and Drug Administration issued the above provisions.
Despite these "negative" news, it did not affect its treatment in the food processing field.
What is the reason for this?
High sweetness is definitely a factor. The sweetness of sodium saccharin is about 500 times that of sucrose. What is the concept? One hundred thousandth of its aqueous solution is sweet! In addition to the taste that can cause sweetness, sodium saccharin does not participate in the metabolism of the human body and does not have any nutritional value for the human body. It is such a nutritionally seemingly insignificant factor that is playing a light weight role, which is related to its non-sugar substance.
Non-sugar substances are simply substances that do not contain sugar compounds. Sugar compounds, or sugars, are what we commonly call carbohydrates. They are nutritious and involved in the metabolism of the human body. Their sugar and calories are high. However, excessive intake can increase the burden on the body. People with diabetes and weight loss are regarded as having a thorn in their eyes. If there is a shortage of sweet substances in life, many foods will hard to swallow.
Therefore, the market needs less calories, sweeteners that do not affect human blood sugar levels and insulin levels, need sugar-free foods, and need sweeteners that can replace natural sugars. The appearance of sodium saccharin is exactly in line with these characteristics. This market demand, or to make up for the "market defects" of sugars.
Afterwards, more sweeteners with similar characteristics to sodium saccharin have appeared in the market. They are mainly divided into the following categories:
One class is non-sugar substances, such as natural non-sugar sweeteners such as licorice, steviol glycosides, and mogroside, as well as sodium cyclohexyl sulfamate (also known as cyclamate) and calcium cyclamate, acesulfame potassium ( Also known as Acesulfame, AK Sugar, and Aspartame (aspartame) artificial sweeteners, they are characterized by a high sugar content, which is several tens to several hundred times that of sucrose. However, they are non-nutritive sweet substances and do not participate in the metabolism of the human body. They use less and have a smaller calorific value.
There is also a class of synthetic sweeteners, called sugar alcohol sweeteners, whose sweetness is similar to sucrose, low sweetness, and nutrient type, but because of its different metabolic processes with glucose, its calorific value is lower, and Does not cause dental caries. Its main varieties are erythritol, D-mannitol, maltitol and maltitol, xylitol, lactitol, sorbitol and sorbitol, isomaltulose, and the like.
Non-sugar natural sweeteners and non-sugar artificial sweeteners, as well as sugar alcohol artificial sweeteners, their calories are small, some even zero calories, do not affect blood glucose levels and insulin levels, can meet the diabetic patients The market demand for low-sugar consumption, etc., is therefore called "sugar replacement." Foods that use them purely can be labeled "sugar-free" on the packaging and are popular with people with diabetes and healthy people.
Despite the high bitterness of food after the high concentration of sodium saccharin, its high sweetness, identity of "sugar substitute", and cost advantages much lower than the price of natural sugars make it widely favored by food companies and sweet as food. Flavoring agents are used in large quantities during food processing, which is why the sodium saccharin is sold well in the market!
However, the abuse of saccharin sodium in the overdose and over-range during the long-term use has also occurred frequently.
In China, some people use saccharin sodium to mix sweet garlic, and others use it to make red wine. These are examples of abuse of sodium saccharin in excess of the scope, and more generally, some manufacturers often have food labels. Not including saccharin sodium and its true content, but concealing the facts with names such as “Protein Sugar†and “Sweet Podâ€, which has caused consumers to mistakenly conceal their rights in violation of their right to know and may also damage their physical health. .
Studies have pointed out that when eating more saccharine, it will affect the normal secretion of digestive enzymes, reduce the intestinal absorption capacity, so that loss of appetite. Consumption of large amounts of saccharin in a short period of time can lead to thrombocytopenia and acute hemorrhage, causing severe damage to the brain, heart, lungs, and kidneys of poisoned people.
A relatively extreme case was described in the book "Live to understand additives." There were brothers and sisters who were 14 and 11 years old. Because they did not understand the difference between saccharin and sugar, they consumed more than 80 tablets of saccharin tablets (about 2 grams of pure saccharin sodium). Soon after, the two people spit foam and wake up. Acute poisoning. The hospital rescue found that poisoning left heart failure, severe pulmonary edema, can not urinate, the brain is also seriously damaged, the hospital diagnosed as a short period of time caused by the intake of large amounts of saccharin.
In view of the adverse effects of sodium saccharin, the Consumers Association of China has solemnly issued warnings on the abuse of sodium saccharin and asked the relevant authorities to study and formulate more stringent use regulations.
Why sodium saccharin can still be used today
It can be said that, along with the controversy over the safety of saccharin use, international research on it has also been carried out. According to years of research, it is safe to use sodium saccharin in accordance with regulations, and saccharin is no longer considered to be human. Health potentially dangerous substances. In the United States, for example, after the FDA withdrew the proposal to ban the use of saccharin in 1991 based on some research results, in December 2010, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency took saccharin and its salts from harmful components and processed them in accordance with the U.S. Resource Protection and Recycling Act. Or remove the list of hazardous commercial chemicals that will be processed.
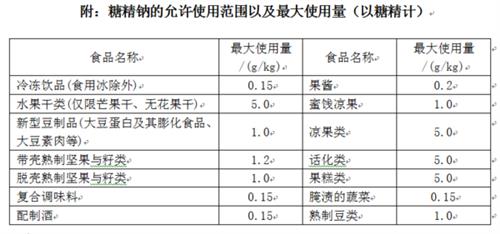
China's new edition of "Standard for the Use of Food Additives" (GB2760-2014) was implemented on May 24, 2015. Compared to the 2011 edition, the scope of use of saccharin sodium in foods has been further reduced in the new version of the food additive use standard, and its use in breads, cakes, biscuits, beverages, and other foods is prohibited. As sweeteners and flavor enhancers, sodium saccharin is allowed to be used in foods such as jams, candied fruits, etc. The maximum amount used is 0.15 to 5 grams per kilogram (see the attached table). The Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) under the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and World Health Organization (JECFA) stipulates that the ADI of saccharin (allowed for daily intake) is 0 to 5 mg per kg body weight per day, that is, 50 kg of body weight per day. The allowable intake is 250 mg. (Part of the data comes from the "Food Additive Use Standards" and "Living Awareness Additives" book, Yu Huixing)
(Author's introduction: Yu Huixing, a famous food and agricultural product expert, has more than 20 years of experience in the management of food and other industries. He has continued to pay attention to social life and the spiritual world for more than 30 years. He has profound cultural heritage. He has been in charge of Zhejiang Jinhua Ham Company and is a media columnist. There is in-depth research and unique insights into the public brands of the food industry and agricultural products, and branding is required to talk about “originality,†and relevant ideas have been widely reported by the media.)
NINGBO VOICE BIOCHEMIC CO. LTD , https://www.medicine-voice.com